< Previous | Contents | Next >
The Climate Crisis & Climate Action for Working People
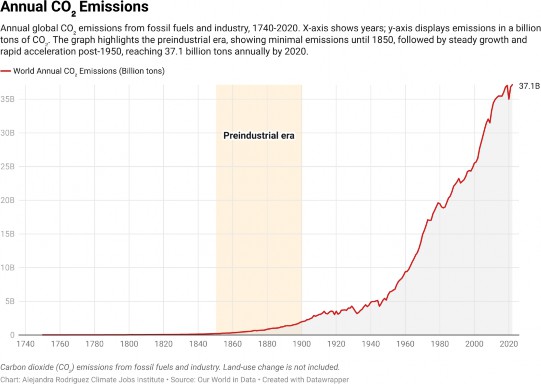
Climate change refers to the rapid warming of the Earth's atmosphere and oceans, and the accompanying shifts in weather patterns, which are primarily driven by human activities– specifically our use of fossil fuels to power our homes, businesses, and transportation systems. Burning fossil fuels like natural gas, coal, and oil releases greenhouse gasses into the atmosphere. Due to its abundance, carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most dangerous greenhouse gas, but methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O),7 and other gasses also pose serious threats.
When released, these gasses trap heat in the atmosphere and cause the planet to warm. Since the pre-industrial era, human activities have significantly increased atmospheric CO2 levels, reaching concentrations not seen in at least 2 million years.8

The global average temperature has increased by approximately 1.0°C (1.8°F) above pre- industrial levels due to human activities.9 To understand the impact of that temperature rise, think about a fever.10 If your body temperature increases by even a single degree, you start to feel feverish and uncomfortable. A five degree rise could send you to the hospital. Without
![]()
7 Calvin et al., “IPCC, 2023.”
8 Jay et al., “Overview: Understanding Risks, Impacts, and Responses.”
9 IPCC, Global Warming of 1.5°C.
10 NASA’s Earth Minute: Earth Has a Fever.
action, average temperatures on earth could increase by 3 to 10 degrees Fahrenheit over the next 70 years.11