The IAM Western Territory
The IAM Western Territory
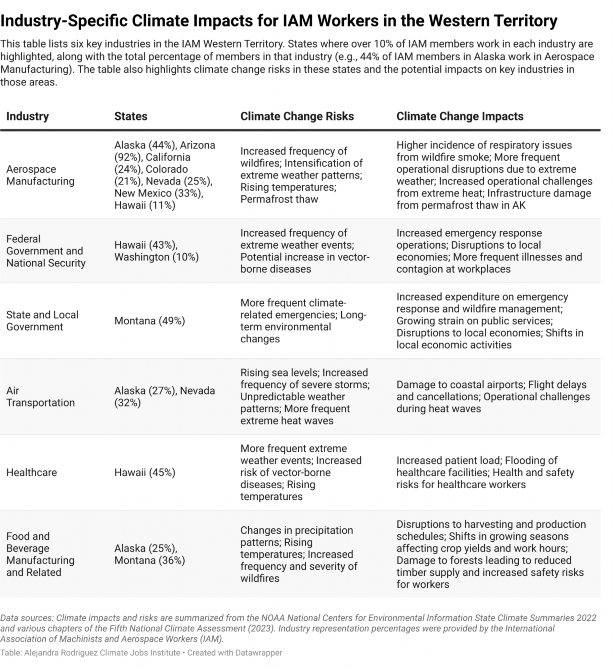
In the IAM Western Territory, Washington and California stand out due to their high number of members, with 42,185 and 37,668 members respectively. These two states are crucial hubs for IAM activities, reflecting their large industrial bases and workforce. Washington is home to Boeing, the largest single employer of IAM members.82
82 International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers, “Western Territory Revised,” June 28, 2024.
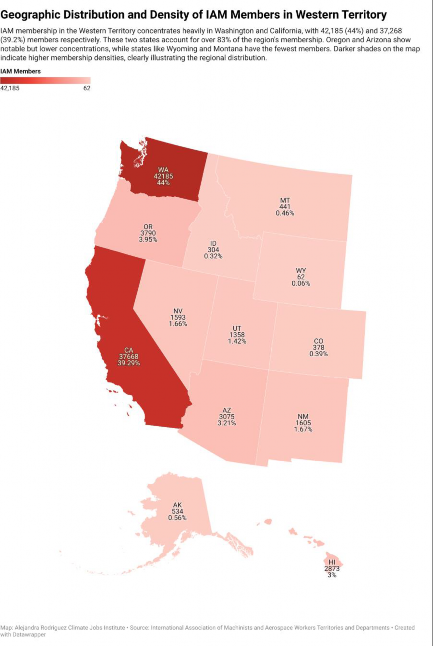
A key feature of the IAM Western Territory is its heavy involvement in the aerospace and aviation industries. Aerospace Manufacturing & Related Services (excluding Airlines) is the dominant sector, accounting for approximately half of the territory’s membership.83
IAM Western Territory Industries
Apart from aerospace and aviation, the Federal Government’s role in National Security is significant, accounting for 7.4% of the IAM’s members in the territory. The Forest Products & Printing sector also plays a substantial role, particularly in states rich in natural resources like Washington, Idaho, and Oregon.84
Climate Change Impacts on the IAM Western Territory
Climate change profoundly affects workers in the IAM Western Territory, impacting health, safety, and job stability across various industries due to its diverse geography and climate zones.
Rising temperatures and more frequent severe weather events pose health risks, particularly for outdoor work and demanding jobs in aerospace, air transportation, and construction. States like Arizona and Nevada face extreme heat that could lead to heat-related illnesses, lower productivity, worsened health conditions, and heat-related deaths.85 For example, in Maricopa County, Arizona, there were 645 heat-related deaths in 2023, representing a 52% increase over 2022.86 In New Mexico and Montana, unpredictable weather may impact agricultural productivity and raw material supply, causing economic instability and potential job losses.87 Extended droughts and wildfires threaten worker safety and disrupt operations.88 In Washington, wildfire smoke might affect aerospace operations, pose respiratory risks, and necessitate advanced air filtration and modified work schedules.
Alaska is warming faster than the global average, leading to significant permafrost thaw that damages infrastructure crucial for aerospace and construction, increasing maintenance costs and operational disruptions. Melting glaciers contribute to sea level rise and altered marine
![]()
84 International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers.
85 White et al., “Chapter 28: Southwest.”
86 Maricopa County Department of Public Health, Division of Epidemiology and Informatics, “2023 Heat Related Deaths Report.”
87 Knapp et al., “Chapter 25: Northern Great Plains.”
88 Chang et al., “Chapter 27: Northwest.”
ecosystems, affecting fisheries and tourism.89 Hawaii also faces rising temperatures and health risks from diseases like dengue fever.90
Industry-Specific Climate Impacts and Implications for IAM Workers in the Western Territory
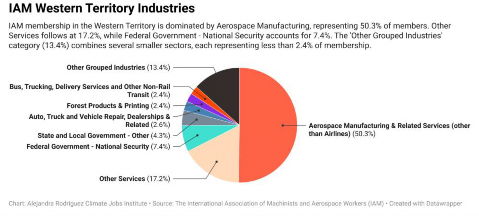
The IAM Western Territory encompasses a diverse range of industries, each uniquely impacted by climate change. These impacts pose significant challenges for workers, affecting their health, safety, and job security. The “Industry-Specific Climate Impacts for IAM Workers in the Western Territory”91 chart provides an analysis of how different industries and states in the IAM Western Territory are affected.
![]()
89 Huntington et al., “Chapter 29: Alaska.”
90 Frazier et al., “Chapter 30: Hawaiʻi and US-Affiliated Pacific Islands.”S
91 International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers, “Western Territory Revised,” June 28, 2024.
Industry-Specific Climate Impacts for IAM Workers in the Western Territory