< Previous | Contents | Next >
Although IAM's Southern Territory is second to the IAM Western Territory in overall membership with 66,011 members in total, every state in the Territory (excepting Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands) has passed so-called "right-to-work" laws.101 These laws are meant to hinder labor's ability to collect dues vital to running their organizations.102 Despite this challenge, the IAM maintains significant membership in the region.103
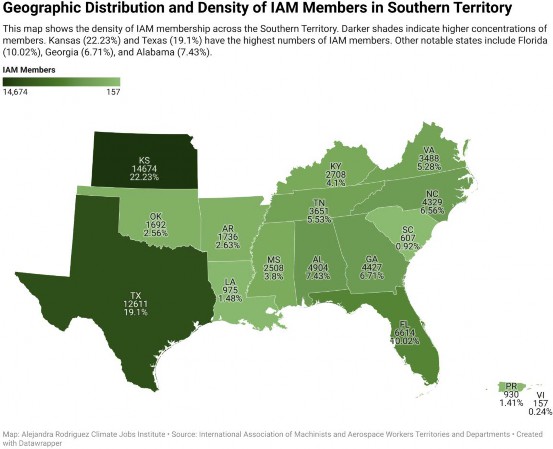
Kansas accounts for 22.23% of all IAM members in the Southern Territory, making it the largest state in terms of membership. The high membership in Kansas is primarily due to the significant aerospace industry presence in Wichita and other parts of the state104 Texas follows with 19.1% of members. Florida and Georgia also have a significant IAM presence.
![]()
101 Sherer and Gould, “Data Show Anti-Union ‘Right-to-Work’ Laws Damage State Economies.”
104 International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers.
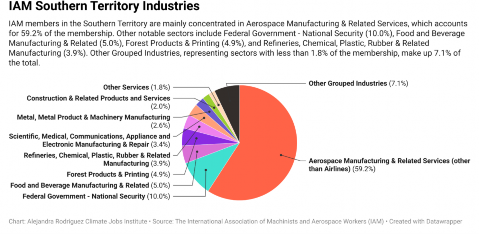
The IAM Southern Territory is heavily influenced by the Aerospace Manufacturing & Related Services sector, which constitutes 59.2% of overall membership.105 The Federal Government - National Security sector also plays a crucial role, making up 10% of membership, reflecting the presence of federal military and security installations. The Food and Beverage Manufacturing & Related sector is also significant, accounting for 5% of IAM members in the territory.
![]()
105 International Association of Machinists and Aerospace Workers.
Climate Change Impacts on the IAM Southern Territory
The IAM Southern Territory, which includes 14 states and the U.S. Caribbean territories of Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands, faces diverse challenges related to climate change. Climate change is causing a range of issues across the Southern Territory, including rising temperatures, shifting rainfall patterns, droughts, wildfires, stronger hurricanes, and flooding.
Coastal areas are experiencing sea level rise and worsening storm surges. Western Gulf Coast sea levels are projected to rise 19–27 inches by 2050. Also, by 2100, with an estimated 3.3 feet rise along the Texas Gulf Coast, a Category 2 hurricane could cause 3–10 times more damage to buildings and result in an additional $10.4 billion in damages (in 2022 dollars). These changes are disrupting ecosystems, threatening water supplies and food production, and endangering communities' health and safety.106 The Caribbean territories are particularly vulnerable to increased storm intensity and sea level rise.107 Along with the Western Territory, IAM members in the Southern Territory may face some of the most diverse and intense climate impacts.
Industry-Specific Climate Impacts and Implications for IAM Workers in the Southern Territory
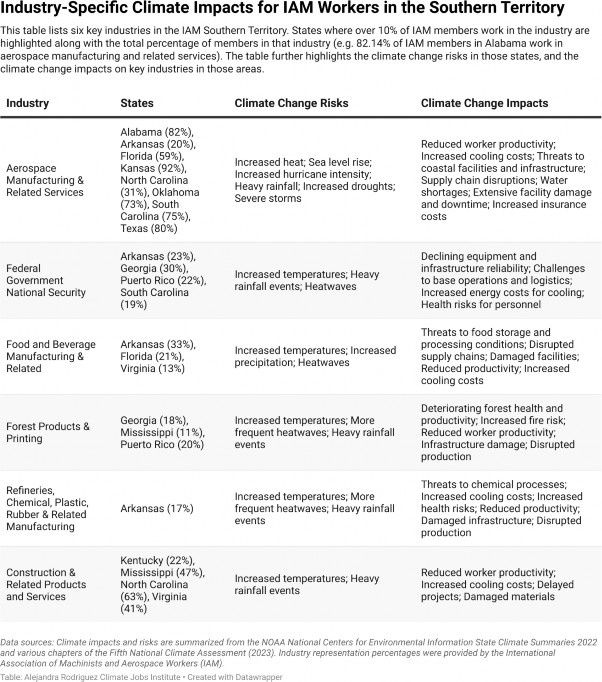
The IAM Southern Territory is home to a wide variety of industries spread across different states, and each of these industries is dealing with its own set of problems caused by climate change. The “Industry-Specific Climate Impacts for IAM Workers in the Southern Territory” table shows the main industries in the region, the states where they have a major presence, and the specific ways that climate change is affecting them.108
![]()
106 McPherson et al., “Chapter 26: Southern Great Plains.”
107 Méndez-Lazaro et al., “Chapter 23: US Caribbean.”